Chaos Engineering is the discipline of experimenting on distributed systems to build confidence in their ability to withstand turbulent conditions. By proactively injecting failures, teams discover weaknesses before they cause outages. Chaos Engineering Principles Build Hypothesis: Define expected system behavior Vary Real-World Events: Simulate realistic failures Run in Production: Test …
Infrastructure Observability and Distributed Tracing Implementation
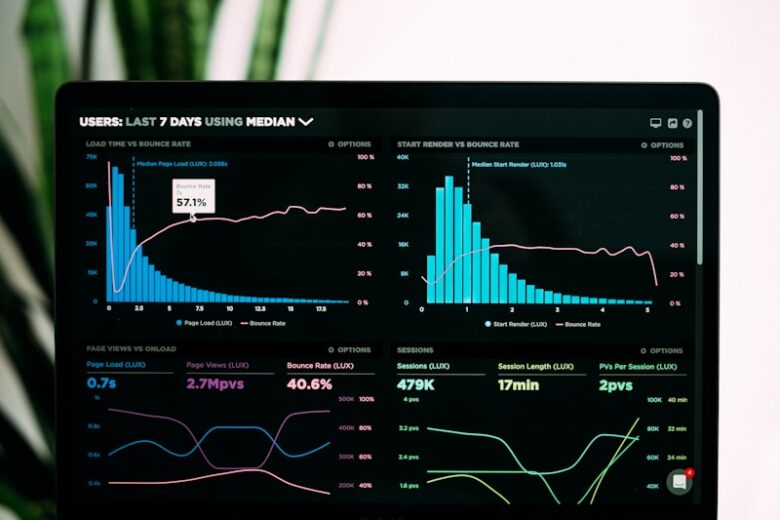
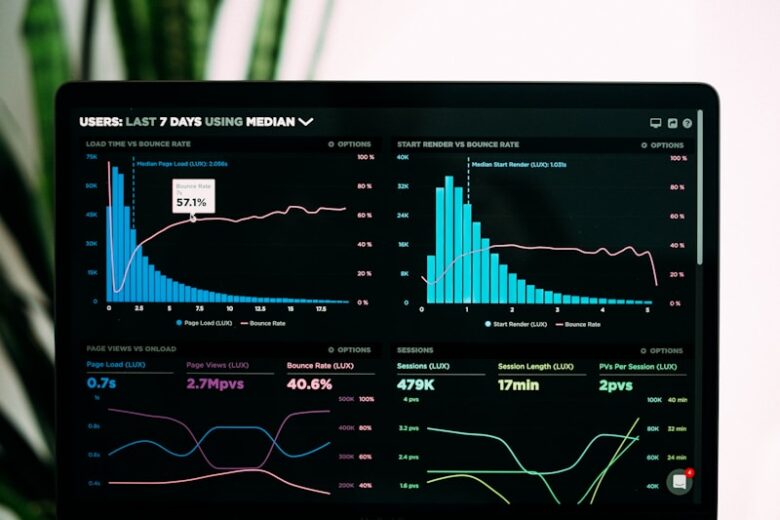
Observability goes beyond traditional monitoring by providing deep insights into system behavior through metrics, logs, and traces. Distributed tracing is essential for understanding request flows across microservices architectures. Three Pillars of Observability Metrics: Numerical measurements over time (latency, error rates) Logs: Discrete events with context Traces: Request journey across services …
Platform Engineering and Internal Developer Platforms (IDP)
Platform Engineering focuses on building and maintaining Internal Developer Platforms (IDPs) that enable self-service capabilities for development teams. By abstracting infrastructure complexity, platform teams accelerate delivery while maintaining governance and security. What is an Internal Developer Platform? An IDP is a layer on top of existing infrastructure that provides developers …
Immutable Infrastructure and Configuration Drift Prevention
Immutable infrastructure is a paradigm where servers are never modified after deployment. Instead of patching existing systems, you replace them entirely with new instances built from a common image. This approach eliminates configuration drift and improves reliability. Benefits of Immutable Infrastructure Consistency: Every deployment is identical Reliability: No configuration drift …
GitOps for Infrastructure Automation: ArgoCD and Flux Implementation
GitOps is an operational framework that uses Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and applications. By storing desired state in Git repositories, teams achieve version control, audit trails, and automated reconciliation of infrastructure. GitOps Principles Declarative: System state is described declaratively Versioned: Desired state is stored …
Kubernetes Security Hardening and CIS Benchmarks Implementation
Kubernetes security hardening involves implementing controls across the cluster, nodes, and workloads. The CIS Kubernetes Benchmark provides a comprehensive framework for securing Kubernetes deployments. This guide covers practical implementation of these security controls. CIS Benchmark Categories Control Plane: API server, controller manager, scheduler, etcd Worker Nodes: Kubelet, container runtime configuration …
Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Encryption Best Practices
Data Loss Prevention and encryption are critical controls for protecting sensitive information in cloud environments. This guide covers implementing DLP policies, encryption strategies, and key management best practices across major cloud providers. Data Classification Before implementing DLP, classify your data into categories: Public: No restrictions on access Internal: Business data, …
Service Mesh Security and Zero Trust Networking with Istio
Service meshes like Istio provide a dedicated infrastructure layer for handling service-to-service communication. They enable zero trust networking by implementing mutual TLS, fine-grained access control, and observability without changing application code. Zero Trust Principles in Service Mesh Never Trust, Always Verify: Authenticate every request Least Privilege Access: Explicit authorization policies …
Cloud Cost Optimization and FinOps Strategies for Engineering Teams
FinOps brings financial accountability to cloud spending by combining systems, best practices, and culture. This guide covers practical strategies for optimizing cloud costs while maintaining performance and reliability. FinOps Framework Phases Inform: Visibility into cloud spending and allocation Optimize: Identify and implement cost reduction opportunities Operate: Continuous governance and improvement …
Container Escape Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Container escapes occur when an attacker breaks out of a container’s isolation to access the host system or other containers. Understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing proper mitigations is critical for container security. Common Escape Vectors Privileged Containers: Running with –privileged flag disables security features Dangerous Capabilities: CAP_SYS_ADMIN, CAP_NET_ADMIN enable escape …
Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) Best Practices
Identity and Access Management is the foundation of cloud security. Properly configured IAM policies prevent unauthorized access and limit the blast radius of security incidents. This guide covers essential IAM best practices for AWS, Azure, and GCP. Principle of Least Privilege Grant only the minimum permissions required for users and …
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security Scanning: Shift-Left Your Cloud Security
Infrastructure as Code security scanning identifies misconfigurations and vulnerabilities in Terraform, CloudFormation, Kubernetes manifests, and other IaC templates before deployment. This shift-left approach prevents security issues from reaching production environments. Why IaC Security Matters Studies show that over 70% of cloud breaches result from misconfigurations. By scanning IaC templates during …